Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Discover how our thoughts influence our behavior and mood
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
A self-fulfilling prophecy is a psychological phenomenon often seen in people. It shows how strongly our actions are influenced by our thoughts.
If we believe we can complete a task or reach a goal, it's likely to happen. Conversely, if we think we can't do something, our chances of success decrease. This is called a self-destructive prophecy. In both cases, we subconsciously achieve the positive feeling of being right.
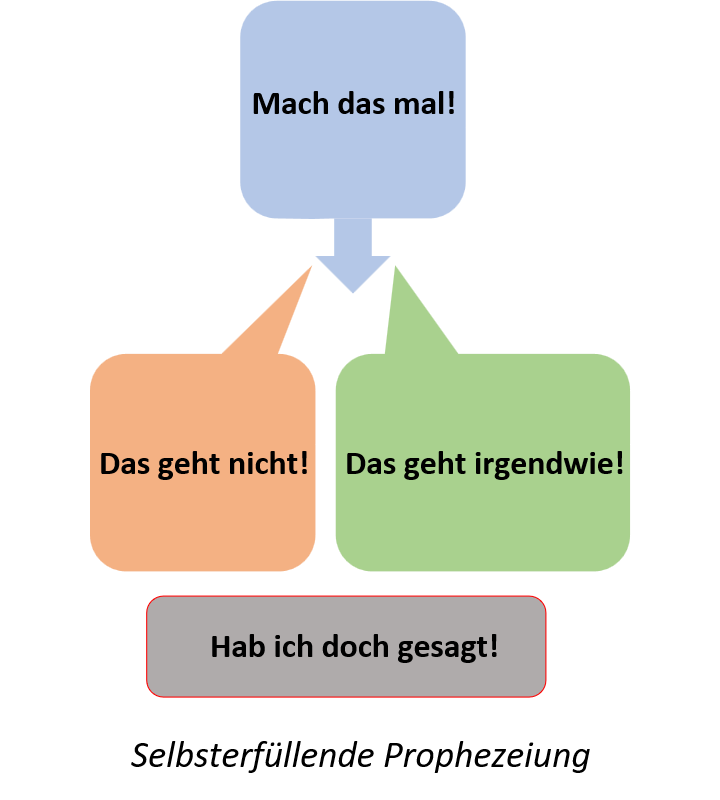
This effect doesn't just work on ourselves; it can also affect others, as the following example shows:
Peter meets Michael at a party. Beforehand, Peter heard some things about Michael. A friend told him that Michael seems a bit odd and unfriendly. With these (prejudiced) thoughts about Michael, they greet each other. Since Peter expects an unfriendly, peculiar person, his greeting is rather cold and reserved. Michael notices this behavior and mirrors it.
This is a natural reaction. It confirms Peter's prejudiced thoughts. That's how a self-fulfilling prophecy works.
This example clearly shows how our thoughts reflect in our behavior. Peter's negative thoughts about Michael influenced his behavior. Michael mirrored this, turning Peter's thoughts into reality and a self-fulfilling prophecy.
In the next example, Peter influences himself with his thoughts:
Peter wants to get his pilot's license. He completes the theory and practice without major issues. Now it's time for the exam. Although Peter knows the material, he gets cold feet. He convinces himself he won't pass. These negative thoughts lead to insufficient preparation. He's also very nervous during the exam. Peter doesn't pass. Again, his thoughts influenced his behavior, making them reality. Yet, Peter was right
But it can also work the other way around:
If Peter repeatedly tells himself before the exam that he's well-prepared and will pass, his chances increase significantly. His positive thoughts lead to thorough preparation and a confident, less nervous exam experience.
Both examples show how our thoughts affect our mood. Negative thoughts ("I can't do this!") make us feel bad. Positive thoughts ("I can do this!") lead to a good mood.
This is also illustrated by the following example:
Peter loves game nights with friends, especially the dice game Yahtzee. Dice games naturally involve a lot of luck, as you can't control how the dice fall.
Peter enters each round with positive thoughts ("I'll roll something good!"). This makes him flexible and creative, so (almost) every roll results in a satisfactory entry, advancing his game. He finds something good in (almost) every roll. Peter's mood is good. His thoughts become reality.
If Peter started with negative thoughts ("The wrong numbers always come up!"), the likelihood of making combination mistakes or missing opportunities increases. Peter's mood is bad. His thoughts become reality.
Conclusion
Never underestimate the power of thoughts, whether negative or positive. Our thoughts influence both our behavior and mood. Fortunately, we can choose what we think.
