Emotional Intelligence
These 5 factors show if you are emotionally intelligent
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence
Everyone has encountered the term "Intelligence Quotient (IQ)" at some point. But few know about the Emotional Intelligence Quotient (EQ). Let's take a closer look at this concept.
Definition
"Emotional Intelligence" refers to the ability to perceive not only your own feelings but also those of others. It's not just about recognizing emotions but perceiving them accurately and influencing them. This involves facial expressions, gestures, and tone of voice.
Origin
The term emotional intelligence was first called "Social Intelligence" in 1920 by American psychologist Edward Lee Thorndike. In the early '90s, psychologists John D. Mayer and Peter Salovey researched "emotional intelligence" and introduced it as a technical term.
The concept gained fame in the mid-'90s through US psychologist and bestselling author Daniel Goleman. He wrote a book on the topic that became a huge international success. The book's title is: EQ. Emotional Intelligence.
Is Emotional Intelligence Measurable?
If you search the internet for EQ tests, you'll find many options. It's up to each person to question the reliability of these tests.
How can emotional intelligence be measured? Like an IQ test, it involves questions that assess social skills.
John D. Mayer and Peter Salovey, along with psychologist David R. Caruso, developed the "Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT)." It's the most commonly used test for assessing EQ.
This test divides a person's EQ into four areas:
Perceiving Emotions
This area is split into perceiving emotions in faces and in designs, landscapes, and pictures. The skills of test-takers differ greatly in these parts.
Using Emotions
There are two sub-areas here. One tests the ability to precisely identify emotions. The other compares emotions with other sensory factors.
Understanding Emotions
This checks how well test-takers can recognize and name multiple emotions in overlapping situations.
Managing Emotions
In this part, test-takers are asked about handling emotions. It determines how well they can change their emotional state (e.g., turning anger into calmness). It also tests the ability to manipulate others' feelings for personal benefit.
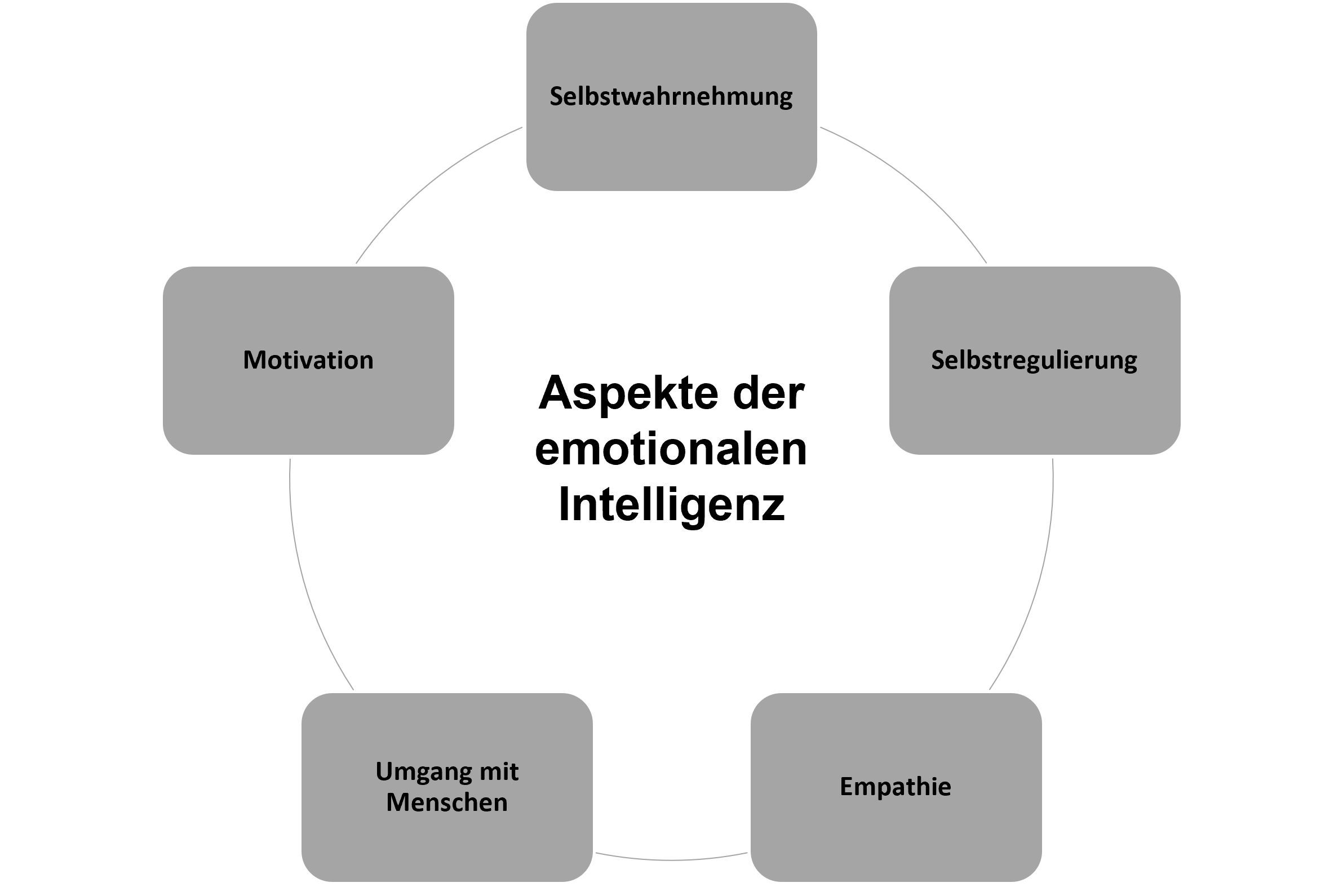
What Constitutes Emotional Intelligence?
According to Goleman, there are five key factors for emotional intelligence:
Self-awareness
This involves being aware of your strengths and weaknesses. In emotional intelligence, it means people with healthy self-awareness can view their feelings and emotions objectively.
Self-regulation
Self-regulation is the ability to control impulses. People with this strength can respond to emotions like anger, frustration, or fear in a controlled way. They don't let emotions solely guide them.
Empathy
Empathy is one of the strongest aspects of emotional intelligence. An empathetic person can put themselves in others' situations and understand their emotions.
Social Skills
This is about the ability to build and maintain relationships with others. Social interaction is essential.
Motivation
This point focuses on intrinsic motivation. It is characterized by passion and ambition for a specific topic. Sticking to a goal despite great obstacles and striving towards it shows high motivation.
Conclusion
The higher a person's emotional intelligence quotient, the greater their inner strength. People with high EQ can handle tough challenges and crises confidently and aren't solely led by emotions.
